Melanoma – Symptoms, causes, and treatment
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, which affects the melanocytes in the human body. Melanocytes are the skin cells which produce melanin, the pigment that gives the skin its color. In melanoma, a mutation in the skin cells causes them to multiply excessively. This overproduction of skin cells often leads to the formation of a mole or a similar growth on the surface of the skin. Let’s take a look at what causes melanoma, know the symptoms of the disease, and explore treatment options.
Symptoms of melanoma
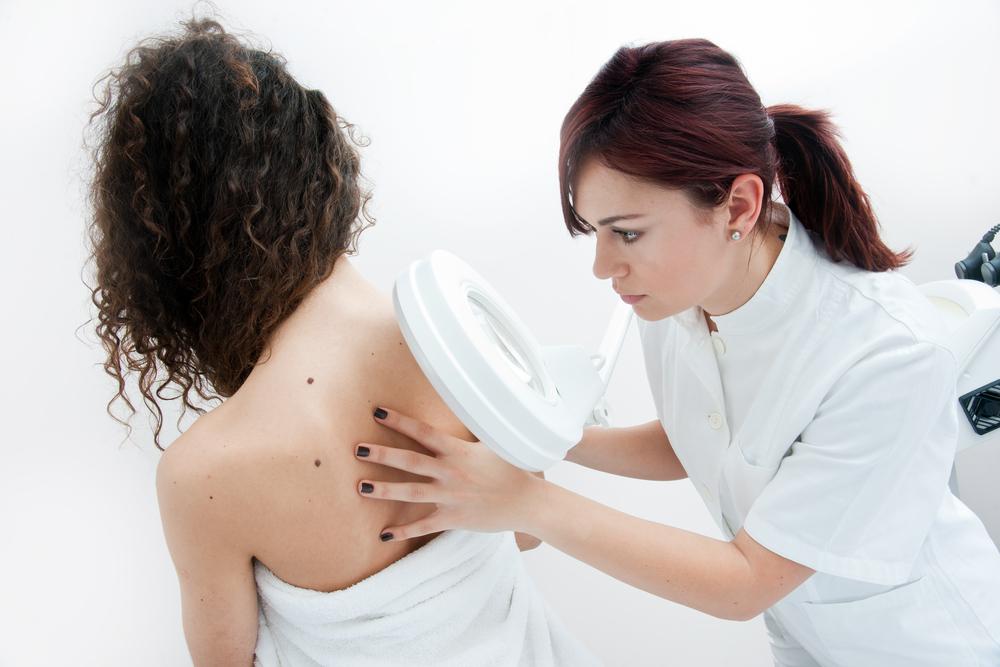
A melanoma mole may appear and develop anywhere on the body. The most common areas for these growths are usually the parts that are exposed to the sun. This includes the face, neck, chest, arms, and legs. However, some people also develop hidden melanoma. A hidden melanoma is one that develops in an area you normally would not check such as under the feet, in the genitals, in the mouth, on the palms, under the nail, on the scalp, and in the eye.
- The initial sign of a melanoma is a sudden change in the size or color of an existing mole.
- Another symptom to watch out for is the sudden appearance of a new mole, which is asymmetrical in shape and seems to keep developing.
Risk factors for developing melanoma
Certain factors increase a person’s chances of developing skin cancer. These factors include are mentioned below.
- Excessive exposure to UV rays and frequent bouts of sunburn
- Excessive use of tanning beds
- A family history of melanoma
- Having a higher-than-average number of moles on the body (The average number of moles on the human body ranges around 50.)
- Living close to the equator belt or living at a higher altitude.
- Having undergone an organ transplant
Diagnosis and treatment
The doctor will examine the mole on your skin to detect if it exhibits cancerous traits or not. However, for an accurate diagnosis, a biopsy is essential. There are three main types of biopsy:
- A punch biopsy in which a small piece of skin is removed from the mole
- An excisional biopsy in which the entire mole is removed
- An incisional biopsy in which only the irregular part of the mole is removed and sent for analysis
- A sentinel node biopsy determines if the melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes
In a post-lab analysis, the doctor will determine the stage of melanoma and then advise a course of treatment.
Treatment options for melanoma may include any one or a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and biological therapy.
Preventive measures
The good news is that by taking certain precautions, you may reduce your risk of developing melanoma:
- Wearing sunscreen while in the outdoors
- Avoiding tanning beds
- Avoiding the sun during the middle of the day, that is between noon and 3 PM.
- Routinely checking your skin for any moles that seem to have grown or changed color