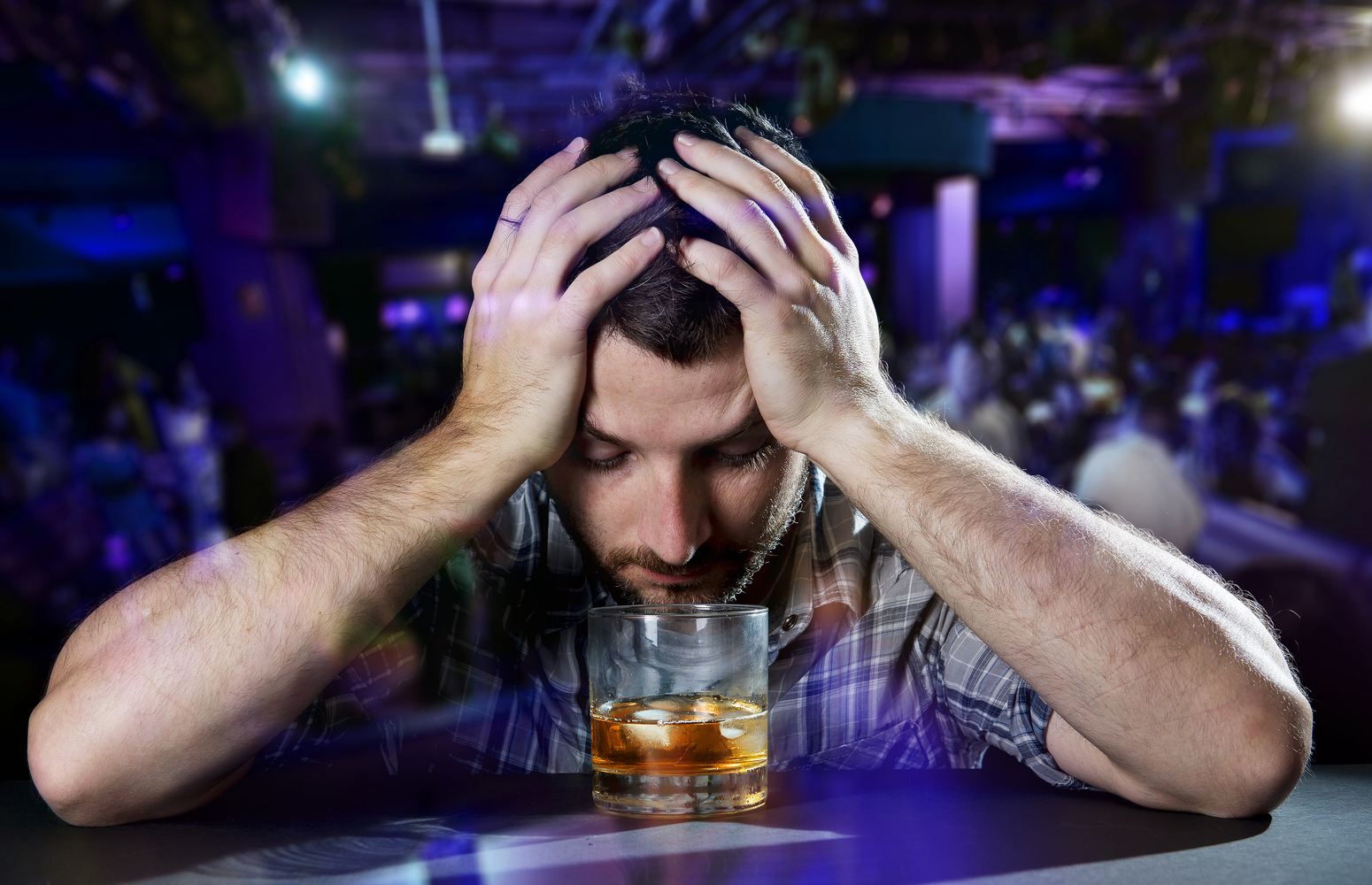
Stages and effects of alcohol addiction
Dependence on alcohol can change a person’s life and have a negative impact on their health, happiness, and financial stability. If they try to stop drinking, they may experience withdrawal symptoms. It is essential to learn about the stages of alcohol addiction and the effect it has on the human body.
Stages of alcohol addiction
- The first stage is characterized by weak psychological dependence. When a person does not have access to alcoholic drinks, the dependence or addiction may disappear.
- The second stage is characterized by the obsessive desire to drink alcohol. Here, alcoholic drinks become a part of life.
- In the third stage, the dependence on alcohol leads to physical symptoms. An individual cannot stop drinking without professional help. If a person stops drinking suddenly, their behavior becomes unpredictable and aggressive. This stage leads to disruptions in the functions of many vital organs.
- In the fourth stage, people may shake and shiver if they don’t have a drink. They continue drinking to avoid these withdrawal symptoms. They may experience physical symptoms like insomnia, tremors, and mood swings because of withdrawal.
Alcohol dependence in the third and the fourth stages cannot be cured without medical help.
Some of the clinical features of alcohol withdrawal are:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Elevated blood pressure
- Excessive sweating and shaking
- Hallucinations
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Seizures
- Agitation
- Shortness of breath
- Dry mouth
- Palpitations
- Confusion
Effects of alcohol addiction on the body
Frequent binge drinking or drinking continuously over time can have a negative impact on an individual’s health. Alcoholism is dangerous as it affects a person’s job and relationships, and it can also have a serious effect on the body. Here are the ways in which alcohols harms the body:
- Brain: Excessive consumption of alcohol can shrink the frontal lobes of the brain. Heavy drinking can cause disruptions in the brain and cause a dramatic change in mood and behavior.
- Mouth, esophagus, and throat: People who drink regularly are more likely to develop throat, mouth, or esophagus cancer. Breast cancer is more common in women who binge drink. Excessive drinking can also damage the tissues of the esophagus.
- Heart: Excessive intake of alcohol damages the heart, resulting in an increase in blood pressure. High blood pressure leads to heart disease and increases the risk of stroke.
- Liver: Over time, heavy drinking can result in chronic alcoholic hepatitis or inflammation. Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can damage the liver, cause liver scarring, and ultimately lead to liver failure.
- Pancreas: Excessive alcohol consumption may lead to chronic pancreatitis, which is a dangerous inflammatory disease that leads to the swelling of the blood vessels in the pancreas.
- Immune system: Heavy drinking weakens the body’s ability to fight off diseases and illness, which can lead to conditions like pneumonia and tuberculosis. It causes other regular problems like numbness, muscle cramps, thinning bones, malnutrition, complications with diabetes, stomach distress, birth defects, infertility, and sexual dysfunction.
It is necessary to seek treatment for alcohol addiction to prevent these health complications and lead a healthy life.